Shrinking Medicaid Rolls In Missouri And Tennessee Raise Flag On Vetting Process

By Phil Galewitz, Kaiser Health News Tangunikia Ward, a single mom of two who has been unemployed for the past couple of years, was shocked when her St. Louis family was kicked off Missouri’s Medicaid program without warning last fall. She found out only when taking her son, Mario, 10, to a doctor to be treated for ringworm. When Ward, 29, tried to contact the state to get reinstated, she said it took several weeks just to have her calls returned. Then she waited again for the state to mail her a long form to fill out attesting to her income and family size, showing that she was still eligible for the state-federal health insurance program for the poor. Mario, who is in third grade, missed much of school in December because Ward could not afford a doctor visit without Medicaid. His school would not let him return without a doctor’s note saying he was no longer infected. In January, with the help of lawyers from Legal Services of Eastern Missouri, she was able to get back on Medicaid, take her son to a doctor and return him to school. “It was a real struggle as it seemed like everyone was giving me the runaround,” Ward said. “I am upset because my son was out of school, and that pushed him behind.” Ward and her children are among tens of thousands of Medicaid enrollees who were dropped by Missouri and Tennessee last year as both states stepped up efforts to verify members’ eligibility. Last year, Medicaid enrollment there declined far faster than in other states, and most of those losing coverage are children, according to state data. State health officials say several factors, including the improved economy, are behind last year’s drop of 7 percent in Missouri and 9 percent in Tennessee. But advocates for the poor think the states’ efforts to weed out residents who are improperly enrolled, or the difficulty of re-enrolling, has led to people being forced off the rolls. For example, Tennessee sent packets to enrollees that could be as long as 47 pages to verify their re-enrollment. In Missouri, people faced hours-long waits on the state’s phone lines to get help in enrolling. Medicaid enrollment nationally was down about 1.5 percent from January to October last year, the latest enrollment data available from the federal government’s Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Herb Kuhn, president and chief executive of the Missouri Hospital Association, said the state’s efforts to verify Medicaid eligibility could be tied to an increase in the number of people without coverage that hospitals are seeing. “When we see over 50,000 children come off the Medicaid rolls, it raises some questions about whether the state is doing its verifications appropriately,” he said. “Those who are truly entitled to the service should get to keep it.” In 2018, Missouri Medicaid began automating its verification system for the state-federal insurance program for the poor. People who were identified as ineligible, for income or other reasons, were sent a letter asking them to provide updated documentation. Those who did not respond or could not prove their eligibility were dropped. The state does not know how many letters it sent or how many people responded, said Rebecca Woelfel, spokeswoman for the Missouri Department of Social Services, which oversees Medicaid. She said Missouri Medicaid enrollees were given 10 days to respond. Woelfel cited the new Medicaid eligibility system, the improved economy and Congress rescinding the federal tax penalty for people who lack insurance as factors behind the decline in enrollment. Missouri’s unemployment rate dropped from 3.7 percent in January 2018 to 3.1 percent in December as the number of unemployed people fell by about 17,000. Missouri Medicaid had almost 906,000 people enrolled as of December, down from more than 977,000 in January 2018, according to state data. About two-thirds of those enrolled are children or pregnant women. Timothy McBride, a health economist at Washington University in St. Louis who heads a Missouri Medicaid advisory board, said the state’s Medicaid eligibility system has made it too difficult for people to stay enrolled. Since low-income people move or may be homeless, their mailing addresses may be inaccurate. Plus, many don’t read their mail or may not understand what was required to stay enrolled, he added. “I worry some people are still eligible but just did not respond, and the next time they need health care they will show up with their Medicaid card and find out they are not covered,” McBride said. Tennessee’s Medicaid enrollment fell from 1.48 million in January 2018 to 1.35 million in December, according to state data. Tennessee Medicaid spokeswoman Kelly Gunderson credits a healthy job market. The state’s unemployment rate was relatively stable last year at under 4 percent. “Tennessee is experiencing a state economy that continues to increase at what appears to be near-historic rates, which is positively impacting Tennesseans’ lives and, in some cases, decreasing their need to access health insurance through the state’s Medicaid” program and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), she said. She added that the state has a “robust appeals process” for anyone who was found ineligible by the state’s reverification system. The Tennessee Justice Center, an advocacy group, has worked with hundreds of families in the past year trying to restore their Medicaid coverage. The verification process will make “Medicaid rolls smaller and saves money, and that’s a poor way for the state to measure success,” said Michele Johnson, executive director of the nonprofit group. “But it’s penny-wise and pound-foolish” because it leads to people showing up at emergency rooms without coverage — and hospitals have to pass on those costs to everyone else. After rapid growth since 2014, when the Affordable Care Act expanded health insurance coverage to millions of Americans, Medicaid enrollment nationally started to fall, declining from 74 million in January 2018 to about 73 million in October, according to the latest enrollment data released by CMS. Missouri and Tennessee are among 17
Analysis: Can States Fix The Disaster Of American Healthcare? (KHN)
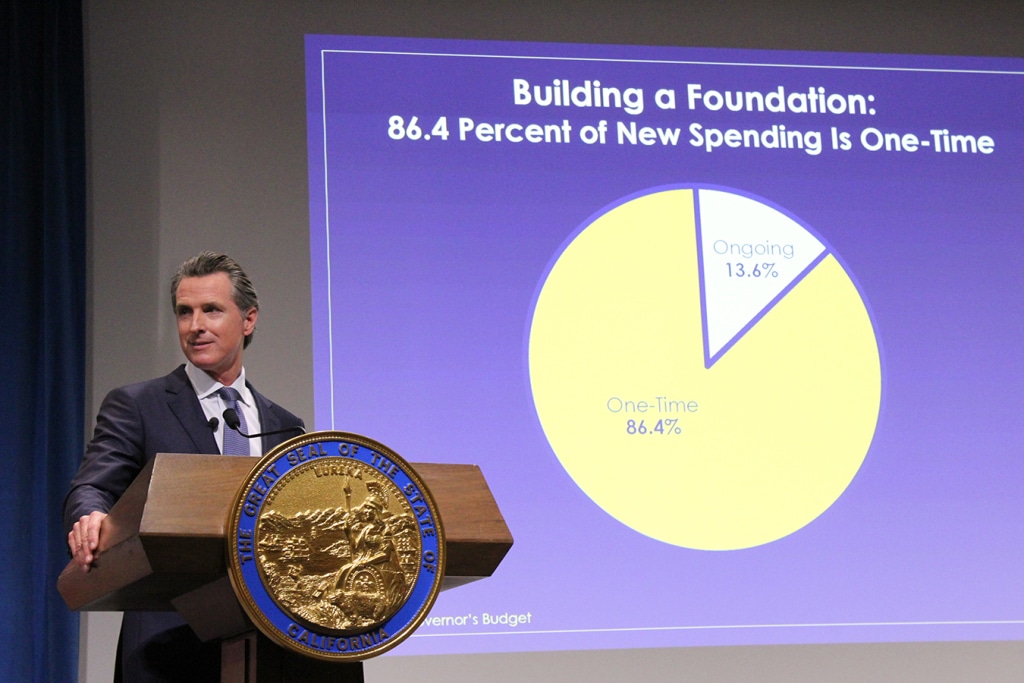
By Elisabeth Rosenthal, Kaiser Health News Last week, California’s new governor, Gavin Newsom, promised to pursue a smörgåsbord of changes to his state’s healthcare system: state negotiation of drug prices, a requirement that every Californian have health insurance, more assistance to help middle-class Californians afford it and healthcare for undocumented immigrants up to age 26. The proposals fell short of the sweeping government-run single-payer plan Newsom had supported during his campaign — a system in which the state government would pay all the bills and effectively control the rates paid for services. (Many California politicians before him had flirted with such an idea, before backing off when it was estimated that it could cost $400 billion a year.) But in firing off this opening salvo, Newsom has challenged the notion that states can’t meaningfully tackle healthcare on their own. And he’s not alone. A day later, Gov. Jay Inslee of Washington proposed that his state offer a public plan, with rates tied to those of Medicare, to compete with private offerings. New Mexico is considering a plan that would allow any resident to buy in to the state’s Medicaid program. And this month, Mayor Bill de Blasio of New York announced a plan to expand healthcare access to uninsured, low-income residents of the city, including undocumented immigrants. For over a decade, we’ve been waiting for Washington to solve our healthcare woes, with endless political wrangling and mixed results. Around 70 percent of Americans have said that healthcare is “in a state of crisis” or has “major problems.” Now, with Washington in total dysfunction, state and local politicians are taking up the baton. The legalization of gay marriage began in a few states and quickly became national policy. Marijuana legalization seems to be headed in the same direction. Could reforming healthcare follow the same trajectory? States have always cared about healthcare costs, but mostly insofar as they related to Medicaid, since that comes from state budgets. “The interesting new frontier is how states can use state power to change the healthcare system,” said Joshua Sharfstein, a vice dean at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and a former secretary of the Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. He added that the new proposals “open the conversation about using the power of the state to leverage lower prices in healthcare generally.” Already states have proved to be a good crucible for experimentation. Massachusetts introduced “Romneycare,” a system credited as the model for the Affordable Care Act, in 2006. It now has the lowest uninsured rate in the nation, under 4 percent. Maryland has successfully regulated hospital prices based on an “all payer” system. It remains to be seen how far the West Coast governors can take their proposals. Businesses — pharmaceutical companies, hospitals, doctors’ groups — are likely to fight every step of the way to protect their financial interests. These are powerful constituents, with lobbyists and cash to throw around. The California Hospital Association came out in full support of Newsom’s proposals to expand insurance (after all, this would be good for hospitals’ bottom lines). It offered a slightly less enthusiastic endorsement for the drug negotiation program (which is less certain to help their budgets), calling it a “welcome” development. It’s notable that his proposals didn’t directly take on hospital pricing, even though many of the state’s medical centers are notoriously expensive. Giving the state power to negotiate drug prices for the more than 13 million patients either covered by Medicaid or employed by the state is likely to yield better prices for some. But pharma is an agile adversary and may well respond by charging those with private insurance more. The governor’s plan will eventually allow some employers to join in the negotiating bloc. But how that might happen remains unclear. The proposal by Washington Gov. Inslee to tie payment under the public option plans to Medicare’s rates drew “deep concern” from the Washington State Medical Association, which called those rates “artificially low, arbitrary and subject to the political whims of Washington, D.C.” On the bright side, if Newsom or Inslee succeeds in making healthcare more affordable and accessible for all with a new model, it will probably be replicated one by one in other states. That’s why I’m hopeful. In 2004, the Canadian Broadcasting Corp. conducted an exhaustive nationwide poll to select the greatest Canadian of all time. The top-10 list included Wayne Gretzky, Alexander Graham Bell and Pierre Trudeau. No. 1 is someone most Americans have never heard of: Tommy Douglas. Douglas, a Baptist minister and left-wing politician, was premier of Saskatchewan from 1944 to 1961. Considered the father of Canada’s health system, he arduously built up the components of universal healthcare in that province, even in the face of an infamous 23-day doctors’ strike. In 1962, the province implemented a single-payer program of universal, publicly funded health insurance. Within a decade, all of Canada had adopted it. The United States will presumably, sooner or later, find a model for healthcare that suits its values and its needs. But 2019 may be a time to look to the states for ideas rather than to the nation’s capital. Whichever state official pioneers such a system will certainly be regarded as a great American. This story originally appeared on Kaiser Health News, and also ran in the New York Times. Kaiser Health News (KHN) is a national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
An Update On Medicaid Expansion Efforts and How They Affect Travelers
As we move closer and closer to November midterm elections in the U.S., healthcare access and quality issues have become a heated political battleground for legislators and citizens across the political spectrum. Medicaid expansion, a tentpole policy part of the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, is one of the key divisive topics in this realm. It’s also something healthcare providers—and by extension travel healthcare professionals—are keeping an eye on, as expansion can have an impact on provider funding and patient care. What Is Medicaid Expansion? Under the Affordable Care Act, states can expand Medicaid eligibility to nonelderly adults with incomes at or below 138 percent of the federal poverty level, which equals about $16,700 a year for a single person and $34,600 for a family of four. Expansion states are funneled billions of dollars from the federal government to support expansion efforts and coverage for newly insured populations. In states that haven’t expanded, those adults fall into a “coverage gap” for having incomes above traditional Medicaid eligibility but below the limit to get approved for ACA marketplace premium tax credits. So far 34 states have approved Medicaid expansion, two states—Maine and Virginia—are in the works to implement expansions, and three states—Idaho, Utah and Nebraska—could potentially approve Medicaid expansion this year. Why is Medicaid expansion important to travelers? Simply put, hospitals in states that expand Medicaid can expect to see a new influx of patients looking for care on a regular basis which can affect seasonal staffing needs. A Commonwealth Fund study in 2015 found that 4 out of 10 primary care physicians who accepted Medicaid saw an increase in patients after expansion coverage took full effect. Additionally, studies have shown that hospitals in expansion states have much healthier budgets, which can leave more money on the table for hiring and retaining temporary or permanent staff. According to an analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation, expansion hospitals saw “significantly improved hospital operating margins.” These factors don’t completely guarantee that facilities in expansion states will overflow with traveler needs, but it can help prevent razor-thin hospital budgets and get executives thinking about how to ease the burden on their permanent staff. What’s happening in states with plans for Medicaid expansion? Maine Medicaid was supposed to be available to newly eligible Maine residents on July 2, but a series of appeals and heated courtroom battles have kept expansion in limbo, leaving more than 70,000 without coverage. At the heart of the issue is Republican Gov. Paul LePage, who has vetoed Medicaid expansion efforts six times in office. Mainers approved Medicaid expansion through a referendum vote with a 59 percent voting majority in 2017, but LePage refuses to submit a plan to the federal government until sufficient state funding—under his terms—is found. LePage was ordered by a Superior Court justice to submit a plan in June, but his administration appealed the ruling to the Maine Supreme Court, saying they did not have to file a plan during the appeal process. Arguments for the appeal took place on July 18, but the court has yet to make a decision. You can view a more detailed timeline of the events leading up to the court hearing by clicking here. Idaho Advocates in Idaho successfully petitioned and gathered 75,314 verified signatures to add a Medicaid expansion measure to the ballot this November. The petition met both state requirements to qualify the ballot measure, gathering at least 56,192 verified signatures that represented at least 18 of Idaho’s 35 legislative districts, according to Ballotpedia. Utah Utah Gov. Gary Herbert signed a bill on March 27, 2018, for partial Medicaid expansion, directing the state to seek federal approval to expand Medicaid to 100% of the federal poverty level. The bill stipulated using the ACA enhanced federal match rate and adding a work requirement for the expansion population. To date, the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has not approved waivers to access the match rate until Utah approves a full expansion. In the meantime, Utah expansion advocates garnered enough petition signatures to add a competing bill to November ballots that would approve a full expansion. Nebraska Similar to Idaho and Utah, Nebraska advocates have submitted a petition to add a Medicaid expansion initiative to the midterm election ballot this fall. Supporters filed more than 133,000 signatures on July 5, but the Secretary of State office is still verifying the signatures. At least 84,908, or more than 60 percent, of the signatures need to be valid for the initiative to make the ballot.
As Maine Medicaid expansion stalls, hospitals and enrollees are left in limbo

Maine’s Medicaid-eligible residents, which make up more than 70,000 people, were set to enroll on July 2 as part of the expansion plan approved by nearly 59 percent of voters last November. But after a month of battles between advocacy groups and stonewalling efforts by Gov. Paul LePage’s administration, the enrollment date has passed and hospitals are left waiting for an influx of patients and staffing needs that may not come anytime soon. “A hospital representative I work with said they all have their fingers crossed that [the expansion] gets approved and it all goes smoothly, but she agreed it is a mess currently,” said Larry Jenkins, a sales team member for staffing agency LiquidAgents Healthcare. “There are no plans for additional staff at this time.” For clarity, here’s a timeline of where Maine’s Medicaid expansion plan stands: November 2017: Maine voters approve Medicaid expansion under provisions outlined in the Affordable Care Act, making Maine the first state to approve expansion by referendum. The Maine Department of Health and Human Services is required to file a plan by April 3, 2018 April 3, 2018: No plan is filed by Maine DHHS. LePage said he would not move forward with a plan until adequate funding is approved by the legislature to support expansion efforts. April 30, 2018: Advocacy group Maine Equal Justice Partners sue Maine DHHS to force the administration to submit a plan, citing a $130 million surplus fund that could be used to fund the expansion for 2019. June 4, 2018: Superior Court Justice Michaela Murphy rules in favor of Maine Equal Justice Partners, citing a “complete failure to act” by Maine DHHS in missing the April 3 deadline. They are ordered to submit a plan by June 11. June 7, 2018: LePage’s administration files an appeal for the decision, and requests to not file a plan by June 11 while the appeal is considered. June 18, 2018: Justice Murphy denies the appeal and orders DHHS again to file a plan with the federal government. Gov. LePage’s legal team appeals the order to the Maine Supreme Judicial Court to delay the deadline while the original appeal is considered. Arguments are scheduled for July 18. June 29, 2018: Gov. LePage vetos a potential expansion funding bill. Lawmakers must decide to override or uphold the veto on July 9. July 2, 2018: Maine Equal Justice Partners encourage eligible residents to apply for Medicaid anyways despite ongoing litigation. July 9, 2018: Conservative legislators uphold the veto in an 85-58 House vote. LePage and House Republicans criticize “one-time” funding sources included in the plan, saying Maine needs a long-term funding plan. Monday’s vote on the veto of Maine’s Medicaid expansion funding bill marks the sixth time LePage has stopped expansion legislation through the use of veto during his two terms of office. The final verdict on Maine’s Medicaid expansion efforts may set the precedent for lawmakers in Idaho, Nebraska and Utah. Advocacy groups submitted similar ballot initiatives after successful petitions to let voters decide the fate of Medicaid in their states this November. Utah’s ballot initiative passed state scrutiny and was added to the fall ballot. Secretaries of state in Nebraska and Idaho are reviewing petition signatures to confirm they represent a specific percentage of voters in each state.
Maine Judge says Gov. LePage must still file Medicaid plan despite appeal

A Maine judge ordered Republican Gov. Paul LePage’s administration to file a Medicaid expansion plan despite ongoing litigation on Monday. The LePage administration made a motion on June 7 to not file a Medicaid expansion plan by June 11 while the Superior Court considers an expedited appeal, which was denied by Superior Court Justice Michaela Murphy on Friday, according to an Associated Press report. Nearly 59 percent of Maine residents voted last fall to expand Medicaid by July 2, which would provide insurance coverage to more than 70,000 adults with incomes at or below 138 percent of the federal poverty level. It would also open the state up to receive more than $500 million in federal funds to cover the new enrollees. The Maine Department of Health an Human Services missed the original April 3 deadline to file the plan and receive these funds, which was cited in the court’s June 4 ruling as a “complete failure to act.” The harm to low-income Mainers who remain without Medicaid benefits outweighs harm to LePage’s administration, Murphy told the Associated Press. “The executive branch’s refusal to act and follow the will of the people … has the potential to engender disrespect for duly enacted laws,” the judge wrote. Gov. LePage vetoed Medicaid expansion legislation five times in two terms of office, saying it will do more harm than good for the state budget and that he considers Medicaid as another form of welfare. His administration laid the blame for not submitting a plan on the state legislature, arguing that they have not found adequate funding to implement the ballot measure, without a tax hike and under LePage’s specific terms. The full cost of implementing the expansion is a disputed figure between Gov. LePage’s administration, which estimates as much as $58 million in the first year, while the nonpartisan Office of Fiscal and Program Review estimates a need of $30 million in state funds.
Judge orders Maine governor to move on Medicaid expansion

Want to know how this will affect traveling healthcare professionals? Click here to read our take on the issue. After months of uncertainty following Maine’s passage of a voter-approved Medicaid expansion effort last year, a state judge on Monday ordered Gov. Paul LePage’s administration to officially move forward with expansion plans. In her ruling, Justice Michaela Murphy of Maine Superior Court ordered the administration to submit a state plan amendment that would update the terms of its Medicaid program and submit it to the federal government by June 11. The ruling cited the “complete failure to act” by Maine Department of Health and Human Services to establish a file a plan to expand Medicaid by the original April 3 deadline. Maine was the first state to expand Medicaid through referendum, and if Gov. LePage’s administration complies by next week, more than 70,000 eligible residents will be able to enroll for healthcare coverage by July 2. It would also trigger a federal cash flow of more than $500 million in federal funds to help the state cover healthcare costs of those with yearly incomes more than 138 percent of the poverty level, which is $16,642 for an individual or $24,600 for a family of four. A spokesperson for Gov. LePage’s administration told Politico that they are reviewing the decision and declined to say if they would appeal the ruling. The court order is a big win for Maine Equal Justice Partners, a progressive group that filed a lawsuit in April to force LePage’s administration to move forward on expansion after DHHS missed the deadline, according to a report in the Bangor Daily News. Gov. LePage has staunchly disapproved of Medicaid expansion efforts, vetoing similar measures multiple times in his two terms of office saying it will burden taxpayers and the state budget. His administration laid blame on the state legislature, arguing that they have not found adequate funding to implement the ballot measure. “Now that Medicaid Expansion is the law, it is my responsibility to implement it, and I will. But until they adequately fund it, there is nothing we can do,” Gov. LePage said in a press release. “Before we can proceed with expansion, DHHS needs both the staff to implement it and the money to pay the bills that will come due when the state plan amendment is approved.” The full cost of implementing the expansion is a disputed figure between Gov. LePage’s administration, which estimates as much as $100 million a year, and the nonpartisan Office of Fiscal and Program Review, which estimated a need of $45 million in state funds. How This Affects Travelers Similar to last week’s announcement that Virginia’s lawmakers successfully passed Medicaid expansion after a five-year battle, the new stream of funding for Maine hospitals could provide a boon to travel employment opportunities in the state. Newly insured patients who may not have had access to healthcare services will flock to hospitals, which could cause a spike in temporary staffing needs. The major difference with Maine, however, is that Maine’s enrollment will begin this summer if the court’s ruling stands, whereas Virginia won’t see an influx in new Medicaid patients until next year. We’ll keep tracking this story as it develops, but keep an eye out in Maine after mid-July and in August for a potential spike in job leads.
Medicaid expansion in Virginia could spur hospital needs, more travel jobs

On the heels of a five-year legislative battle, Virginia lawmakers voted to expand Medicaid this week, which is poised to bring in thousands of new patients to hospitals and, in turn, a potential for increased temporary staffing needs across state hospitals. The Virginia Senate, which is controlled by a Republican majority, voted Wednesday to approve a state budget expanding Medicaid, and the House of Delegates, which originally opposed the expansion, approved it shortly afterward. Democratic Gov. Ralph Northam is expected to sign the budget soon. Nearly $2 billion in federal funds that were up for grabs in previous years will now funnel into state facilities and help provide insurance coverage for an estimated 400,000 low-income residents. Under the Affordable Care Act, the Virginia Medicaid expansion will target citizens with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level—$16,643 for an individual and $28,700 for a family of three. Those who qualify will be able to enroll at the start of 2019. Newly insured citizens could cause growth in patient demand, which, in turn, could lead to increased temporary staffing needs in the state, said Sheldon Arora, CEO of travel nurse staffing agency LiquidAgents Healthcare. Many studies have shown states that expand Medicaid programs under the ACA also see a marked growth in Medicaid enrollment, according to findings published by the Kaiser Family Foundation. Additionally, a 2015 study by The Commonwealth Fund found that primary care physicians who accepted Medicaid reported seeing an increased number of Medicaid patients. “Underserved groups will use healthcare services frequently because they have never had insurance or haven’t had insurance in a while. When they get it, they’ll use it,” Arora said. “We should expect the demand to increase, because hospitals may not have the staff to take care of the influx in new patients, so they will have to get more help from temporary nurses.” Other states looking to expand Medicaid Virginia will be the 33rd state to approve Medicaid expansion, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation, but several other states are also working towards expansion approval. Utah Utah residents will vote on a November referendum to further expand Medicaid to serve an additional 150,000 residents. Idaho Medicaid expansion was added to the November ballot after roughly 58,000 Idaho residents signed a ballot proposal in May. State officials are still verifying that all the signatures came from 6 percent of the registered voters in at least 18 of Idaho’s 35 legislative districts. Nebraska Nebraska Democrats started a grassroots campaign encouraging voters to sign a petition to get Medicaid expansion on the November ballot. Organizers have until July 5 to gather 85,000 signatures.
